How to Choose the Best Farm Fertilizer for Your Crops?
Choosing the right farm fertilizer can be overwhelming. With so many options available, farmers often struggle to make informed decisions. According to Dr. Emily Carter, an expert in agronomy, "Selecting the proper farm fertilizer is crucial for maximizing crop yields." This highlights the importance of understanding fertilizer's role in agriculture.
Farm fertilizers vary in composition and purpose. Some are designed for specific crops, while others provide general nutrients. Farmers must consider soil health, crop needs, and environmental impact. For instance, organic fertilizers can improve soil quality over time. However, they may not provide immediate nutrient boosts like chemical options do.
Farmers also face the challenge of balancing cost and effectiveness. High-quality fertilizers can be expensive. Yet, using low-quality products can lead to poor crop performance. Reflecting on past choices can help improve future decisions. Seeking expert advice is crucial in this evolving field. Proper research and consideration can lead to better harvests and sustainability.
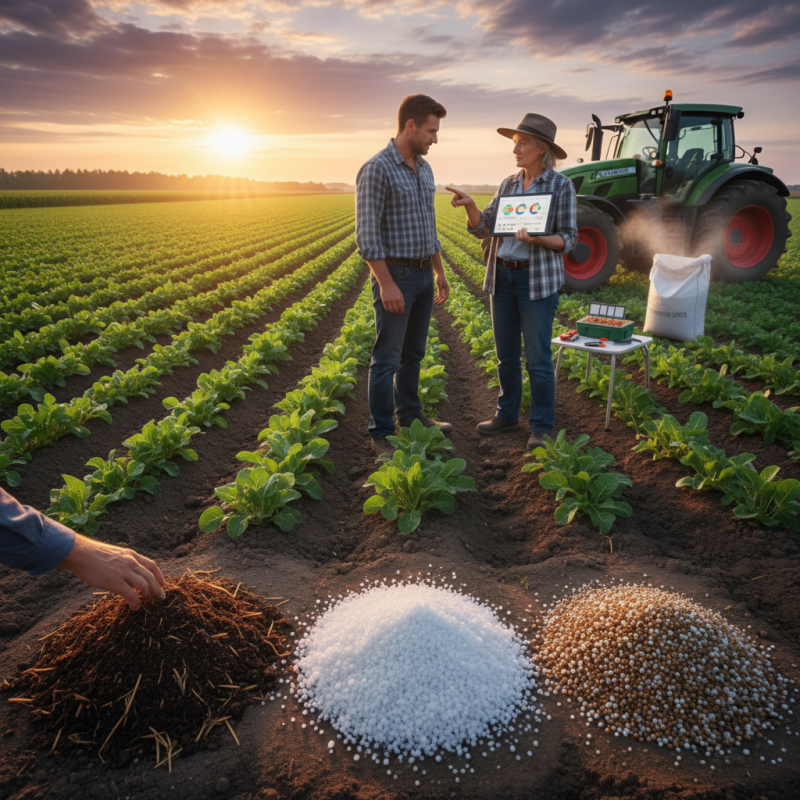

Understanding Soil Nutrients and Their Importance for Crop Health
Understanding soil nutrients is vital for crop health. Different crops require varying levels of nutrients. These include nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium. Each nutrient plays a unique role. For example, nitrogen promotes leafy growth, while phosphorus enhances root development. Potassium is critical for overall plant health and resilience.
Soil tests can help identify nutrient deficiencies. Farmers often skip this step, leading to unbalanced fertilization. Over-fertilizing can harm the soil ecosystem. It’s essential to amend the soil with the right nutrients in appropriate amounts. Observing how crops respond can guide future applications. Some farmers may realize they're using too much nitrogen but neglect other important minerals.
Micronutrients, often overlooked, can significantly affect crop yields. Zinc, copper, and iron are necessary in small amounts but crucial for many plant functions. Recognizing the symptoms of deficiencies in crops is important. For instance, yellowing leaves can signal nitrogen deficiency. Mixing these insights with regular soil assessments can help improve plant health and productivity.
Understanding Soil Nutrients for Crop Health
Types of Fertilizers: Organic vs. Inorganic Options and Their Benefits

When choosing fertilizer, understanding the differences between organic and inorganic options is crucial. Organic fertilizers come from natural sources like compost, manure, and plant materials. They improve soil health by enhancing its structure and increasing microbial activity. These fertilizers release nutrients slowly, providing a steady supply to plants over time. However, they sometimes have lower nutrient concentrations. This might not meet the immediate needs of fast-growing crops.
Inorganic fertilizers, on the other hand, contain synthetic chemicals. They usually offer a quick release of nutrients, which can boost crop growth rapidly. This approach has its downsides too. Overuse can lead to soil degradation and water pollution. The choice isn’t clear-cut. A farmer might notice that plants respond differently to each type. Some crops thrive on organic options, while others may require additional inorganic nutrients. Balancing both types could be the key to a successful harvest, but it requires careful observation and adjustments.
Analyzing Soil Composition and Nutrient Deficiencies in Your Fields
Understanding soil composition is crucial for effective farming.
Soil pH, organic matter, and nutrient levels determine crop yield. According to the USDA, 70% of U.S. soils are low in organic matter. This deficiency can severely impact growth and productivity.
Analyzing soil samples regularly helps identify specific nutrient needs.
Testing can reveal deficiencies in nitrogen, phosphorus, or potassium.
For example, a recent study found that 40% of corn fields lacked adequate nitrogen. This deficiency can lead to stunted growth and decreased yield.
Farmers should consider applying correctional fertilizers based on these findings.
It's easy to overlook these details, yet they are vital. Even seasoned farmers can underestimate soil health.
Relying solely on general fertilizers might not address specific soil needs.
A tailored approach based on precise soil analysis often leads to better results. Regular assessments prevent costly mistakes and maximize productivity.
Determining Application Rates and Timing for Maximum Crop Yield

Timing and application rates are crucial for maximizing crop yield. According to the USDA, appropriate fertilization can increase yields by up to 30%. However, many farmers fail to adjust their application based on soil tests. Neglecting soil health often leads to nutrient imbalances. This can adversely affect crop growth.
Researchers suggest that applying fertilizers in split doses can enhance nutrient uptake. For instance, using 50% of the required nitrogen at planting and the rest during the growing season can be more effective. The local climate also plays a role in determining the best timing. Crops in warmer regions may need earlier applications compared to cooler areas.
Farmers should consider weather patterns. Rainfall can influence nutrient leaching, especially with nitrogen. It's essential to monitor conditions closely. An over-application of fertilizer may not only waste resources but also harm the environment. While aiming for high yields, careful management of application rates is necessary to ensure sustainability. Balancing immediate crop needs with long-term soil health remains a challenge for many in the industry.
Best Practices for Fertilizer Application and Environmental Considerations
When applying fertilizers, timing is crucial. Soil tests can guide you in understanding nutrient needs. Applying at the wrong time can harm crops. Fertilizer leaching often occurs during heavy rains. This can lead to nutrient loss and environmental damage.
Choosing the right application method matters. Broadcasting can be quick, but it risks uneven distribution. A more targeted approach, like banding, can enhance efficiency. However, it requires more equipment and precision. Be mindful of the surrounding ecosystem. Over-fertilization can disrupt local water sources and soil health.
Integrating organic methods can be beneficial. Cover crops help improve soil structure and nutrient availability. They reduce fertilizer dependency over time. Regularly reassess your practices. What worked last season may not be effective now. This reflection can lead to better results and a healthier farm.
How to Choose the Best Farm Fertilizer for Your Crops?
| Fertilizer Type | Primary Nutrients | Application Rate (lbs/acre) | Best For | Environmental Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Urea | Nitrogen (N) | 100-300 | Cereal Crops | Risk of leaching |
| Triple Superphosphate | Phosphorus (P) | 50-150 | Root Vegetables | Potential runoff |
| Potassium Sulfate | Potassium (K) | 100-200 | Fruits & Vegetables | Heavy metal accumulation |
| Compost | N-P-K (varies) | 1-10 | All types of crops | Sustainable, low risk |
| Organic Fertilizers | N-P-K (varies) | 20-80 | Crops seeking organic status | Lower environmental impact |
Related Posts
-
Find the Best Local Fertilizer Shops Near Me for 2025 Gardening Success
-
Top Benefits of Using Ag Fertilizer for Optimal Crop Growth?
-

Top 10 Best Fertilizer Companies You Should Know?
-

Why Do Fertilizer Manufacturers Focus on Sustainable Practices?
-

Find the Best Fertilizer Shop Near Me for All Your Gardening Needs
-

Why Choose an Organic Fertilizer Company for Sustainable Farming?
