What is a Laboratory Sample Pulverizer and How Does It Work?
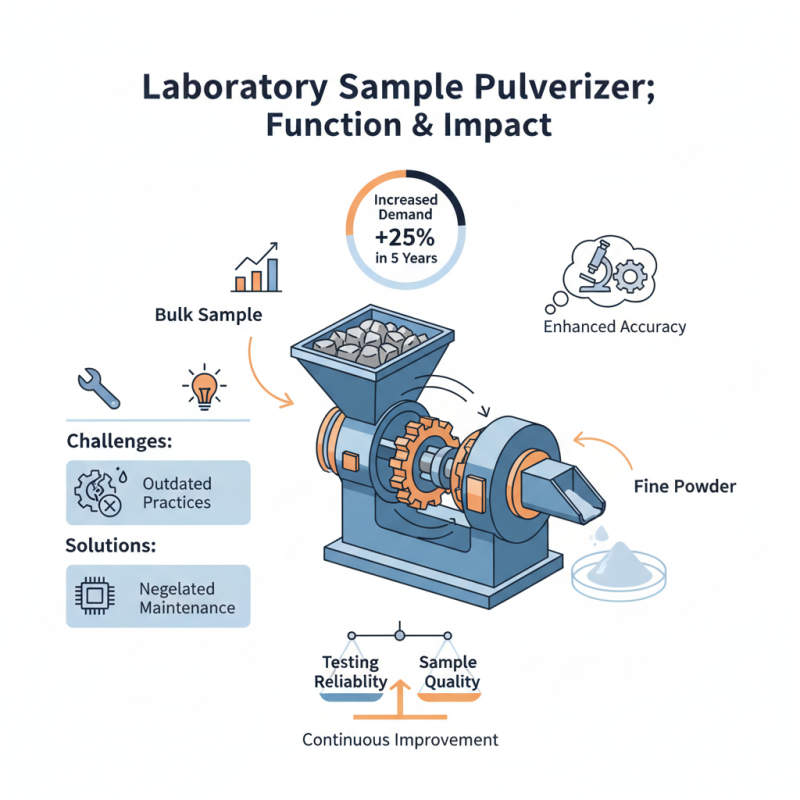
In the world of materials testing, the term "laboratory sample pulverizer" holds significant weight. This crucial equipment is essential for reducing bulk samples into finer powders for analysis. A recent industry report from the Materials Testing Association noted that the demand for efficient pulverization tools has increased by over 25% in the past five years. This rising need reflects advancements in testing methodologies and the growing emphasis on precision.
Dr. Emily Chen, a renowned expert in material science, emphasizes the importance of quality in pulverization. She stated, "An efficient laboratory sample pulverizer can greatly enhance the accuracy of material analysis." Despite this, some laboratories still struggle with outdated pulverizing practices, leading to potential data inaccuracies. It’s concerning that many facilities overlook maintenance, a critical element for optimal performance. Incorporating modern pulverization technologies can mitigate these issues.
The laboratory sample pulverizer not only aids in size reduction but also plays a pivotal role in ensuring sample homogeneity. As industries evolve, continuous investment in better pulverizing techniques becomes paramount. However, the challenge lies in adopting these advancements while addressing unique material properties. This balance is essential for improving testing reliability and quality in various fields.
Overview of Laboratory Sample Pulverizers
Laboratory sample pulverizers serve a crucial role in material analysis. These machines crush and grind samples into fine powders. This process helps scientists and engineers test materials accurately. Commonly, they are used in geology, metallurgy, and environmental studies.
The machines use various methods to pulverize samples. Some employ mechanical force, while others use impact or attrition. Each method has its merits and flaws. A poorly adjusted pulverizer might not achieve the desired particle size. Re-calibration is often necessary to ensure precision.
Users must consider sample properties and desired outcomes carefully. Different materials respond uniquely to grinding. It’s essential to experiment with settings. An optimized pulverization technique can lead to more accurate test results. However, this process requires patience and practice. Trial and error may be part of the journey.
Laboratory Sample Pulverizer Usage by Material Type
Types of Laboratory Sample Pulverizers
Laboratory sample pulverizers are essential tools in various fields, including geology, environmental science, and materials testing. These devices crush and grind samples to prepare them for analysis. The design of pulverizers can vary significantly, impacting their efficiency and suitability for different types of materials.
Among the commonly used types of laboratory sample pulverizers are disc mills, hammer mills, and ball mills. Disc mills use two opposing discs to crush material. They are efficient for fine grinding, especially for brittle samples. Hammer mills, on the other hand, utilize high-speed rotating blades to shred materials. They are great for softer samples but may struggle with harder ones.
Ball mills are known for their adaptability. These machines grind materials by placing them in a rotating container with balls. The action can be modified based on the sample's characteristics. However, each type of pulverizer has its limitations. For instance, some may require frequent maintenance or lead to contamination. It's crucial to choose the right one based on your sample and specific needs.
Laboratory Sample Pulverizer Types and Specifications
| Type | Application | Material | Capacity (kg/hr) | Power (kW) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Disk Mill | Non-metallic minerals | Quartz, Clay | 50 | 5.5 |
| Mortar and Pestle | Organic samples | Herbs, Seeds | 1 | N/A |
| Roller Mill | Metallurgical samples | Ores, Alloys | 100 | 7.5 |
| Hammer Mill | Wood and biomass | Wood Chips, Straw | 200 | 15 |
| Ball Mill | Mineral processing | Iron Ore, Gold | 300 | 22 |
Principles of Operation of a Sample Pulverizer
A laboratory sample pulverizer is an essential tool in material testing. It works by reducing large samples into smaller particles. These particles can then be analyzed accurately in various experiments. The device typically employs mechanical energy to break down materials through grinding or crushing.
The principles of operation revolve around the interaction between the sample and the mechanism. The sample is placed into the pulverizer. As it operates, blades or hammers strike the sample repeatedly. This high-speed action results in a fine powder. The design may vary, but the core concept remains the same.
Tips: Ensure the sample size suits the pulverizer’s specifications. Too large a sample may lead to uneven grinding. Regular maintenance is crucial. Worn parts can affect efficiency and create inconsistencies in results.
Even with proper use, there may be issues. Sometimes, the particle size can be uneven. This might require additional processing. Remember to calibrate your device regularly. Calibration can greatly improve your outcome and enhance accuracy in your analysis.
Applications of Laboratory Sample Pulverizers
Laboratory sample pulverizers play a vital role in various applications. They are used to crush and grind samples into fine powders. This process helps in preparing materials for further analysis. Different industries utilize these devices, including mining, geology, and material science.
In the mining sector, pulverizers are essential for analyzing ore samples. They enable precise evaluations of mineral content. Geologists benefit from these tools by preparing rock samples for testing. It aids in understanding geological formations. Material scientists use pulverizers to create composite materials. The ability to achieve a homogenous blend is crucial in research and product development.
However, some challenges exist. Choosing the right pulverizer can be tricky. Factors like sample size and hardness matter. Sometimes, the process can introduce contamination, which skews results. Users need to be aware of these potential pitfalls. Careful maintenance of the equipment is also necessary to ensure accuracy. Overall, laboratory sample pulverizers are integral to numerous applications but require thoughtful consideration.
Maintenance and Safety Considerations for Pulverizers
Maintaining a laboratory sample pulverizer is critical to ensure efficient operation. Regular cleaning is necessary to prevent contamination. Dust and debris can lead to inaccurate results. The American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM) recommends protocols for periodic inspection. Worn-out parts should be replaced immediately. Neglecting maintenance can lead to costly downtime.
Safety considerations are equally important when operating pulverizers. Wearing appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) like gloves and goggles is essential. A report from the National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH) highlights the risks of noise and dust exposure. Over 80% of workers reported irritation after working without proper safeguards. Users must be aware of these conditions to promote a safe working atmosphere.
Training operators on safety protocols is crucial. Misuse can result in accidents, leading to injuries or damage to equipment. Regular training updates help reinforce safety standards. However, many facilities overlook refresher courses. This can create hazardous situations. Implementing a culture of safety is key for any laboratory using pulverizers.
